Table of Contents
Introduction to Product Positioning
1.1 Understanding Product Positioning in E-Commerce
Product positioning in e-commerce is the strategic process of defining where your product stands in the market and how it is perceived by your target customers. This involves determining the unique value your product offers and how it differentiates from competitors. In the dynamic and competitive online retail landscape, mastering product positioning is essential for capturing customer interest and driving sales.
Consider the example of Warby Parker, an online retailer of prescription glasses and sunglasses. Warby Parker disrupted the traditional eyewear market by positioning itself as a provider of stylish, high-quality, and affordable eyewear. Their direct-to-consumer model, combined with a home try-on program, highlighted convenience and value, effectively positioning them against established, higher-priced brands like Ray-Ban.
1.2 The Importance of Product Positioning in Marketing
Product positioning is a cornerstone of successful marketing strategies in e-commerce. It helps businesses communicate the distinct benefits of their products, making them more appealing to potential customers. A well-positioned product can create a strong brand image, foster customer loyalty, and drive long-term business growth.
Statistics show that 59% of shoppers prefer to buy from brands they trust. Effective product positioning builds this trust by clearly communicating what the brand stands for and why its products are worth purchasing. For instance, Apple positions its products around innovation, quality, and design. This clear and consistent positioning has helped Apple maintain a loyal customer base and command premium prices.
1.3 Key Concepts and Terminology
To master product positioning in e-commerce, understanding key concepts and terminology is vital:
- Unique Selling Proposition (USP): This is what sets your product apart from competitors. It’s the unique benefit or feature that makes your product stand out. For example, Dollar Shave Club’s USP was delivering high-quality razors at a fraction of the price of traditional brands, with the convenience of home delivery.
- Target Market: The specific group of consumers you aim to reach with your product. Identifying your target market helps tailor your positioning strategy to meet their specific needs and preferences. For example, Glossier targets millennials and Gen Z with its minimalist beauty products and strong social media presence.
- Brand Positioning Statement: A succinct statement that encapsulates your product’s value, target market, and unique benefits. This statement guides your marketing and branding efforts, ensuring consistency across all channels.
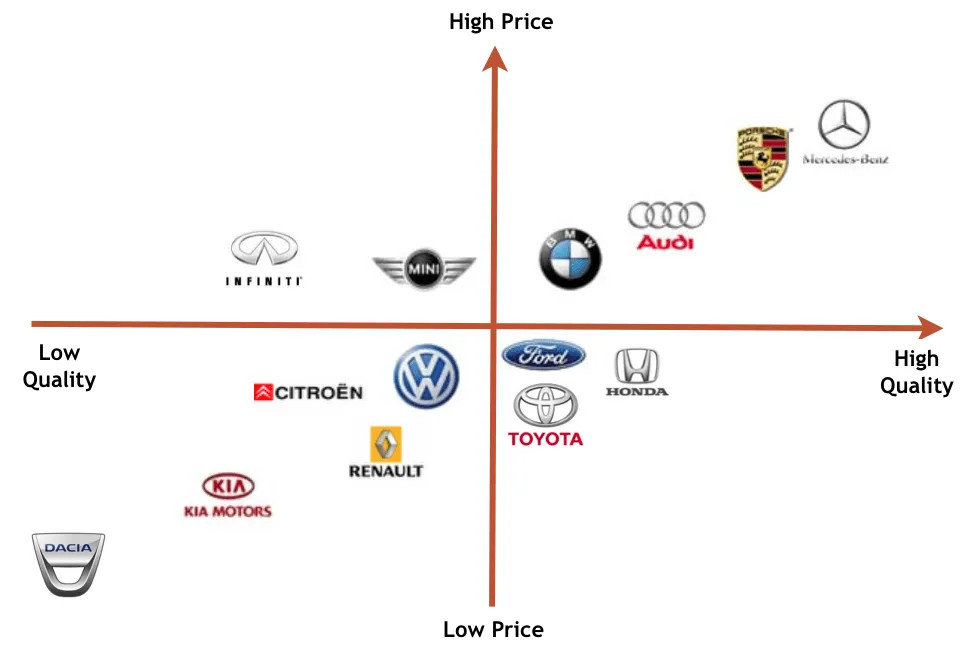
- Positioning Map: A visual representation that shows how your product compares to competitors based on key attributes such as price, quality, and features. This helps identify gaps in the market and opportunities for differentiation.
By understanding and leveraging these concepts, new e-commerce entrepreneurs can develop robust positioning strategies that resonate with their target audience and drive business success.
Mastering product positioning in e-commerce involves defining your product’s unique value, clearly communicating this to your target market, and consistently reinforcing this message through all marketing efforts. This strategic approach can help your online store stand out in a crowded market, attract loyal customers, and achieve sustainable growth.
Developing a Product Positioning Strategy

2.1 Steps to Develop a Product Positioning Strategy
Creating a robust product positioning strategy involves a series of well-planned steps to ensure your product stands out in the e-commerce market. Here’s a detailed guide to help you navigate this process:
- Identify Your Target Market: Start by defining who your ideal customers are. Use demographic, geographic, psychographic, and behavioral data to create detailed customer profiles. Tools like Google Analytics and Facebook Audience Insights can provide valuable information.
- Analyze Your Competition: Conduct a thorough competitive analysis to understand your competitors’ strengths and weaknesses. Identify their USPs and positioning strategies. This analysis helps you find gaps in the market where your product can thrive.
- Define Your Unique Selling Proposition (USP): Your USP is the unique benefit or feature that sets your product apart from the competition. This could be anything from superior quality and innovative features to better customer service or lower prices. For instance, TOMS Shoes’ USP is its one-for-one giving model, which resonates with socially conscious consumers.
- Craft Your Brand Positioning Statement: Create a concise statement that defines your product’s value, target market, and key benefits. This statement should guide all your marketing and branding efforts. An example could be: “For eco-conscious consumers, our reusable water bottles provide a stylish and sustainable way to stay hydrated on the go.”
- Communicate Your Positioning: Ensure that your product positioning is consistently communicated across all marketing channels, including your website, social media, email campaigns, and advertising. Use compelling storytelling to connect with your audience emotionally.
- Test and Refine: Launch your product and gather feedback from customers. Use this feedback to refine your positioning strategy, making adjustments as needed to better meet the needs and expectations of your target market.
2.2 Role of Market Segmentation in Product Positioning
Market segmentation is the process of dividing a broad consumer or business market into sub-groups based on shared characteristics. Effective segmentation allows you to tailor your product positioning strategy to meet the specific needs of different segments.
- Demographic Segmentation: Based on age, gender, income, education, and other demographic factors. For example, a luxury online store may target high-income individuals aged 30-50.
- Geographic Segmentation: Based on location, such as country, city, or neighborhood. An online shop selling beachwear may focus on coastal regions.
- Psychographic Segmentation: Based on lifestyle, values, and personality. For instance, a brand like Patagonia targets environmentally conscious consumers.
- Behavioral Segmentation: Based on purchasing behavior, usage rate, and brand loyalty. An e-commerce site might segment customers into frequent buyers, occasional buyers, and first-time visitors.
By understanding these segments, you can create tailored positioning strategies that resonate more deeply with each group, improving your chances of converting them into loyal customers.
2.3 Competitive Analysis for Positioning
A comprehensive competitive analysis is crucial for effective product positioning. This involves:
- Identifying Competitors: List direct and indirect competitors in your market. Tools like SEMrush and Ahrefs can help identify competitors and analyze their strategies.
- Analyzing Competitor Products: Evaluate the features, benefits, pricing, and marketing strategies of competitor products. Look for strengths and weaknesses in their positioning.
- Understanding Market Gaps: Identify opportunities where competitors are not fully meeting customer needs. This can be an area where your product can excel.
- Benchmarking: Compare your product’s performance against competitors. Use metrics like market share, customer satisfaction, and brand loyalty to gauge where you stand.
For example, when launching its smartphone, OnePlus positioned itself against premium brands like Apple and Samsung by offering high-end features at a mid-range price, targeting tech-savvy consumers looking for value for money.
2.4 Creating a Positioning Map
A positioning map, also known as a perceptual map, is a visual tool that shows how your product compares to competitors based on key attributes. This helps identify where your product fits in the market and highlights areas for differentiation.
- Select Attributes: Choose two attributes that are important to your target market, such as price and quality or innovation and convenience.
- Plot Competitors: Place your competitors on the map based on how they score on these attributes.
- Identify Gaps: Look for areas on the map where there are few or no competitors. These gaps represent opportunities for differentiation.
- Position Your Product: Place your product on the map based on its attributes. Ensure it occupies a unique space that sets it apart from competitors.
For instance, a positioning map for the online grocery market might plot “price” on the x-axis and “convenience” on the y-axis, showing how various brands like Amazon Fresh, Walmart, and Instacart compare.
Example Positioning Map
| High Price | Low Price | |
| High Quality | Brand A | Your Product |
| Low Quality | Brand B | Brand C |
This positioning map highlights that your product is positioned as a low-price, high-quality option, filling a market gap.
Identifying Target Markets

3.1 Market Segmentation and Positioning
Market segmentation is a foundational step in developing a successful product positioning strategy for your e-commerce business. By dividing the broader market into smaller, more manageable segments, you can tailor your marketing efforts to meet the specific needs of each group, thereby enhancing your product’s appeal and effectiveness.
Types of Market Segmentation:
- Demographic Segmentation: This involves categorizing the market based on variables such as age, gender, income, education, and occupation. For instance, a luxury online store might focus on high-income professionals aged 30-50.
- Geographic Segmentation: This method segments the market based on location, such as country, region, or city. An e-commerce business selling winter sports equipment might target customers in colder climates.
- Psychographic Segmentation: Here, the market is divided based on lifestyle, values, and personality traits. Brands like Patagonia use this approach to target environmentally conscious consumers who prioritize sustainability.
- Behavioral Segmentation: This involves segmenting the market based on purchasing behavior, usage rate, and brand loyalty. An online retailer could segment its market into frequent buyers, occasional buyers, and first-time visitors, offering tailored promotions to each group.
By understanding these segmentation types, you can more effectively position your products to meet the unique needs of each market segment. For example, Nike uses behavioral segmentation to target professional athletes with high-performance gear, while also marketing casual sportswear to fitness enthusiasts.
3.2 Identifying and Analyzing Target Markets
Identifying and analyzing target markets involves a series of steps to ensure you understand who your customers are and what they need. This knowledge allows you to position your products in a way that resonates with them.
Steps to Identify and Analyze Target Markets:
- Conduct Market Research: Use surveys, focus groups, and online analytics tools to gather data about potential customers. Tools like Google Analytics and Facebook Insights can provide valuable demographic and behavioral information.
- Develop Customer Profiles: Create detailed profiles of your ideal customers, including their demographics, preferences, and pain points. This helps you tailor your product positioning to address their specific needs.
- Analyze Competitors: Study your competitors to understand who their customers are and how they are positioning their products. This analysis can reveal gaps in the market that your product can fill.
- Use Data Analytics: Leverage data analytics to identify trends and patterns in customer behavior. Platforms like HubSpot and Salesforce can help you track customer interactions and refine your target market segments.
For example, when launching its subscription box service, Birchbox identified its target market as young, busy professionals who enjoy discovering new beauty products but lack the time to shop for them. By tailoring its product positioning to this segment, Birchbox quickly gained a loyal customer base.
3.3 Customer-Centric Positioning
Customer-centric positioning is about placing the customer at the heart of your product positioning strategy. It involves understanding your customers’ needs, desires, and pain points, and positioning your product as the best solution.
Principles of Customer-Centric Positioning:
- Empathy: Put yourself in your customers’ shoes to understand their challenges and needs. Use this insight to shape your product and its messaging.
- Personalization: Tailor your marketing messages and product offerings to individual customer segments. Personalized marketing has been shown to increase consumer engagement and loyalty.
- Value Proposition: Clearly articulate the unique value your product offers to the customer. This should address their specific needs and highlight how your product solves their problems better than competitors.
- Consistent Messaging: Ensure that your positioning is consistently communicated across all customer touchpoints, including your website, social media, email campaigns, and customer service interactions.
For example, Zappos, an online shoe and clothing retailer, excels at customer-centric positioning by offering free shipping and returns, a 365-day return policy, and exceptional customer service. This focus on customer satisfaction has earned Zappos a reputation for reliability and quality, attracting a loyal customer base.
Customer-Centric Positioning in Action:
- Amazon: Amazon’s positioning revolves around customer convenience, offering a vast selection of products, competitive pricing, and fast delivery options. This customer-centric approach has helped Amazon dominate the e-commerce market.
- Spotify: Spotify positions itself as the go-to music streaming service by offering personalized playlists and recommendations based on user preferences and listening history, enhancing the user experience.
By focusing on customer-centric positioning, e-commerce businesses can build strong relationships with their customers, foster loyalty, and drive long-term growth.
Differentiating Your Products

4.1 Differentiation and Product Positioning
Differentiating your products is a critical aspect of effective product positioning in e-commerce. Differentiation involves identifying and promoting the unique characteristics and benefits of your products that set them apart from competitors. This not only helps in attracting and retaining customers but also in establishing a strong brand presence in the online marketplace.
Why Differentiation Matters:
- Increased Customer Loyalty: Differentiated products create a unique value proposition that resonates with customers, fostering loyalty and repeat purchases.
- Reduced Price Sensitivity: Unique products often face less price competition because customers perceive them as offering greater value.
- Enhanced Brand Image: Differentiation helps build a distinct brand identity, making it easier for customers to remember and prefer your brand over others.
4.2 Market Differentiation Strategies
There are several strategies to differentiate your products in the e-commerce landscape. Here are some effective approaches:
- Quality and Innovation: Offering superior quality or innovative features can set your product apart. For example, Dyson differentiates its vacuum cleaners with advanced technology and sleek design.
- Customization: Providing customization options can make your products more appealing. Nike’s “Nike By You” allows customers to design their own shoes, creating a personalized shopping experience.
- Unique Selling Proposition (USP): Define a clear USP that highlights a unique benefit of your product. For instance, TOMS Shoes’ “One for One” model, where a pair of shoes is donated for every pair purchased, appeals to socially conscious consumers.
- Exceptional Customer Service: Offering outstanding customer service can be a significant differentiator. Zappos is renowned for its customer-centric policies, such as free returns and 24/7 customer support, which contribute to its strong brand loyalty.
- Sustainability: Emphasizing eco-friendly practices and products can attract environmentally conscious consumers. Brands like Patagonia and Allbirds have successfully differentiated themselves by prioritizing sustainability.
4.3 Brand Differentiation Techniques
Building a differentiated brand involves more than just offering unique products. It encompasses the entire customer experience and how your brand is perceived. Here are some techniques to achieve effective brand differentiation:
- Consistent Branding: Ensure your brand messaging, visual identity, and tone of voice are consistent across all touchpoints. Consistency builds brand recognition and trust. Apple’s minimalist design and clear messaging are examples of effective brand consistency.
- Emotional Connection: Create an emotional connection with your audience by telling compelling stories and aligning with their values. For example, Dove’s “Real Beauty” campaign focuses on body positivity and self-esteem, resonating deeply with its target audience.
- Community Building: Foster a community around your brand to create a sense of belonging among your customers. Glossier, a beauty brand, leverages its community by encouraging customers to share their experiences and feedback, creating a loyal and engaged customer base.
- Influencer Partnerships: Collaborate with influencers who align with your brand values to reach a wider audience and enhance credibility. Daniel Wellington, a watch brand, grew its presence significantly through strategic influencer marketing.
- Innovative Marketing Campaigns: Stand out with creative and innovative marketing campaigns. Old Spice’s humorous and memorable “The Man Your Man Could Smell Like” campaign revitalized the brand and differentiated it in a crowded market.
Real-Life Example:
- Warby Parker: This eyewear brand differentiates itself with a home try-on program, stylish designs, and affordable prices. Additionally, its social mission of donating a pair of glasses for every pair sold enhances its appeal to socially conscious consumers.
Differentiating your products and brand is essential for standing out in the competitive e-commerce landscape. By leveraging quality, customization, a strong USP, exceptional customer service, sustainability, consistent branding, emotional connections, community building, influencer partnerships, and innovative marketing campaigns, you can create a compelling and unique brand identity that attracts and retains customers.
Crafting a Positioning Statement

5.1 How to Write a Product Positioning Statement
A positioning statement is a concise description of your target market and a compelling picture of how you want that market to perceive your brand. It’s a critical element of your overall marketing strategy as it guides the direction of your messaging and branding efforts. Here’s how to craft an effective product positioning statement:
- Identify Your Target Audience: Clearly define who your product is for. This involves understanding your market segmentation and creating detailed customer personas.
- Define the Market Category: Specify the market in which your product competes. This helps set the context for your positioning statement.
- Highlight the Unique Benefit: Articulate the unique value or benefit your product offers. This should address a specific need or solve a particular problem for your target audience.
- Provide Supporting Evidence: Include any key features, attributes, or reasons that substantiate your claim. This reinforces the credibility of your unique benefit.
Example Process:
- Target Audience: Young professionals aged 25-35 who prioritize convenience and health.
- Market Category: Ready-to-eat meals.
- Unique Benefit: Offers gourmet, nutritious meals delivered to your door.
- Supporting Evidence: Chef-prepared, organic ingredients, delivered within 30 minutes.
Positioning Statement: “For young professionals seeking convenience and health, our ready-to-eat meals offer gourmet, nutritious options delivered to your door. Each meal is chef-prepared using organic ingredients and delivered within 30 minutes, ensuring you never compromise on quality or convenience.”
5.2 Examples of Successful Product Positioning Statements
To better understand how to craft a powerful positioning statement, let’s look at some successful examples from leading brands:
- Apple iPhone: “For individuals who want the best in mobile technology, the Apple iPhone offers unparalleled innovation, design, and functionality. Unlike other smartphones, the iPhone integrates seamlessly with your life and other Apple products, providing a superior user experience.”
- Tesla Model S: “For eco-conscious consumers who desire luxury and performance, the Tesla Model S offers an exhilarating driving experience with zero emissions. Combining cutting-edge technology, exceptional range, and advanced safety features, it redefines what an electric car can be.”
- Slack: “For teams that need to collaborate efficiently, Slack is a messaging app that brings all your communication together in one place. Unlike traditional email, Slack allows for real-time messaging, file sharing, and integrations with other tools, making teamwork simpler and more productive.”
5.3 Positioning Statement Framework
To create a compelling and concise positioning statement, you can use the following framework:
[Target Audience] – Describe the specific group of customers you are targeting.
[Market Category] – Define the market in which your product competes.
[Unique Benefit] – Articulate the primary benefit or value your product provides.
[Supporting Evidence] – Provide reasons or features that substantiate the unique benefit.
Template Example:
- For [target audience], who need [market category], [product name] is a [unique benefit] that [supporting evidence].
Example Using the Framework:
- For busy parents, who need nutritious meal options, HelloFresh is a meal delivery service that provides pre-measured ingredients and easy-to-follow recipes, helping you cook healthy meals in under 30 minutes.
Crafting a clear and compelling positioning statement is crucial for guiding your marketing and branding efforts in the competitive world of e-commerce. By identifying your target audience, defining your market category, highlighting your unique benefit, and providing supporting evidence, you can create a positioning statement that effectively communicates your product’s value and differentiates it from competitors.
Implementing Product Positioning

6.1 Product Placement Strategy in the Market
Implementing a product placement strategy is essential for ensuring that your product reaches the right audience at the right time. This involves strategically positioning your product within the market to maximize visibility and appeal. Here’s how to do it:
- Channel Selection: Choose the right sales channels to reach your target market. For instance, if you’re targeting millennials, leveraging social media platforms like Instagram and TikTok can be highly effective. If your product is a B2B solution, consider LinkedIn and industry-specific forums.
- Strategic Partnerships: Collaborate with other brands and businesses that complement your product. This can enhance your product’s reach and credibility. For example, a health food brand might partner with fitness influencers or gyms to promote their products.
- Search Engine Optimization (SEO): Optimize your product listings with relevant keywords to improve search engine rankings. This increases the likelihood of your product being discovered by potential customers. Tools like Google Keyword Planner can help identify high-traffic keywords.
- Paid Advertising: Use targeted ads to reach specific segments of your market. Platforms like Google Ads and Facebook Ads allow for detailed targeting based on demographics, interests, and behaviors. For example, a luxury skincare brand might target ads to high-income individuals who follow beauty and wellness pages.
6.2 Effective Product Positioning Techniques
To implement your product positioning strategy effectively, consider the following techniques:
- Storytelling: Use compelling stories to connect with your audience emotionally. This can make your product more memorable and relatable. Brands like TOMS Shoes use storytelling to highlight their social mission, creating a strong emotional connection with consumers.
- Content Marketing: Create valuable content that educates and engages your audience. This can include blog posts, videos, and social media updates. For instance, a company selling eco-friendly products might produce content on sustainability tips and environmental impact.
- Customer Testimonials and Reviews: Leverage positive customer feedback to build trust and credibility. Encourage satisfied customers to leave reviews and share their experiences. According to a survey by BrightLocal, 87% of consumers read online reviews for local businesses.
- Influencer Marketing: Partner with influencers who align with your brand values and have a significant following among your target market. Influencer endorsements can significantly boost your product’s visibility and credibility.
- Personalization: Offer personalized experiences to your customers. This can include personalized product recommendations, marketing messages, and customer service. Personalization can increase customer satisfaction and loyalty.
6.3 Product Branding and Identity
Building a strong brand identity is crucial for successful product positioning. Your brand identity should reflect your product’s unique value and resonate with your target audience. Here’s how to develop and maintain a compelling brand identity:
- Brand Values and Mission: Clearly define your brand’s core values and mission. This will guide all your branding efforts and help create a consistent and authentic image. For example, Patagonia’s commitment to environmental sustainability is central to its brand identity.
- Visual Identity: Develop a cohesive visual identity that includes your logo, color scheme, typography, and overall design aesthetic. This helps create a recognizable and memorable brand. Apple’s sleek and minimalist design is a prime example of effective visual branding.
- Brand Voice and Messaging: Establish a distinct brand voice that reflects your brand’s personality. Whether it’s friendly, professional, or humorous, your brand voice should be consistent across all communication channels. Mailchimp, for example, uses a friendly and approachable tone in its messaging.
- Customer Engagement: Actively engage with your customers through social media, email, and other channels. Respond to their queries, listen to their feedback, and show appreciation for their support. Building strong relationships with your customers can enhance brand loyalty.
- Consistency: Ensure that all aspects of your branding, from your website to your packaging, are consistent. This creates a unified brand experience and reinforces your brand identity.
Case Study: Glossier
Glossier, a beauty brand, has successfully implemented these strategies to build a strong brand identity and effectively position its products in the market. By focusing on simplicity, transparency, and community engagement, Glossier has created a loyal customer base and a distinctive brand image. Their use of social media to engage with customers and gather feedback has been particularly effective in reinforcing their brand identity.
Implementing a product positioning strategy requires a thoughtful approach to product placement, effective positioning techniques, and strong branding. By selecting the right channels, leveraging storytelling, creating valuable content, and building a consistent brand identity, you can ensure your product stands out in the competitive e-commerce market.
Evaluating and Refining Your Positioning

7.1 Positioning Analysis and Reassessment
Product positioning is not a one-time task but an ongoing process that requires regular analysis and reassessment to stay relevant in the dynamic e-commerce market. Evaluating your product positioning involves examining how your product is perceived by your target audience and how it stands against competitors. Here’s how you can perform an effective positioning analysis:
- Customer Feedback: Regularly gather and analyze customer feedback through surveys, reviews, and direct interactions. Tools like SurveyMonkey and Google Forms can help collect valuable insights. Understanding customer perceptions and satisfaction can reveal strengths and areas for improvement.
- Sales Data Analysis: Review your sales data to identify trends and patterns. Metrics such as conversion rates, average order value, and customer retention rates provide insights into how well your product is performing in the market.
- Market Trends: Stay updated with market trends and shifts in consumer behavior. This can help you anticipate changes in demand and adjust your positioning strategy accordingly. Industry reports from sources like Statista and Nielsen can provide valuable market insights.
- Competitor Analysis: Continuously monitor your competitors’ strategies and market positioning. Tools like SEMrush and Ahrefs can help you track competitor activities and identify opportunities for differentiation.
Learn more about customer feedback in e-commerce.
Learn how to conduct market research for digital demand in e-commerce.
7.2 Positioning and Repositioning Strategies
Based on the findings from your positioning analysis, you may need to refine your current strategy or even reposition your product entirely. Here are some strategies for positioning and repositioning:
- Re-emphasize Unique Value: If your product’s unique selling proposition (USP) is losing impact, reinforce its unique benefits through updated marketing messages and campaigns. Highlight any new features or improvements to remind customers of your product’s value.
- Target New Segments: If your current market segment is saturated or not responding well, consider targeting new customer segments. For example, expanding from a younger demographic to include older age groups or different geographic regions.
- Adjust Pricing Strategy: Sometimes, repositioning involves changing your pricing strategy to better align with market expectations. This could mean adopting a premium pricing model if you enhance your product’s perceived value or offering discounts and promotions to attract cost-sensitive customers.
- Enhance Brand Experience: Improve the overall customer experience by enhancing product quality, customer service, and post-purchase support. This can help reposition your brand as a leader in customer satisfaction and reliability.
- Rebrand: In some cases, a complete rebranding might be necessary. This involves changing your brand’s visual identity, messaging, and positioning to better resonate with your target audience.
7.3 Case Studies on Product Positioning Strategies
Examining real-world examples can provide valuable insights into effective product positioning strategies and the impact of repositioning efforts.
Case Study: Old Spice
Old Spice, a well-known brand in the men’s grooming market, successfully repositioned itself from an outdated brand to a trendy, modern choice for young men. The “The Man Your Man Could Smell Like” campaign utilized humor and bold advertising to capture the attention of a younger demographic. This repositioning not only revitalized the brand but also significantly increased sales and market share.
Key Takeaways:
- Bold Advertising: Innovative and memorable ads can change brand perception.
- Target Audience Shift: Successfully targeting a new demographic can revitalize a brand.
Case Study: LEGO
LEGO faced declining sales in the early 2000s due to changing market dynamics and competition from digital entertainment. The company repositioned itself by focusing on creativity and educational value, appealing to both children and adults. Collaborations with popular franchises like Star Wars and Harry Potter also helped attract a broader audience.
Key Takeaways:
- Educational and Creative Focus: Emphasizing educational benefits can attract parents and educators.
- Strategic Partnerships: Collaborations with popular franchises can expand market reach.
Case Study: Airbnb
Airbnb repositioned itself from a budget travel option to a platform offering unique and personalized travel experiences. The “Live There” campaign highlighted the authenticity and local flavor of Airbnb accommodations, appealing to travelers seeking immersive experiences rather than standard hotels.
Key Takeaways:
- Experience-Based Marketing: Promoting unique experiences can differentiate a brand from traditional competitors.
- Personalization: Highlighting personalized travel options can attract a diverse customer base.
Evaluating and refining your product positioning is crucial for maintaining relevance and competitiveness in the e-commerce market. Regular analysis, customer feedback, and staying attuned to market trends can inform necessary adjustments or complete repositioning strategies. Learning from successful case studies can provide inspiration and practical insights into effective positioning tactics.
Advanced Positioning Strategies

8.1 Emotional vs. Functional Positioning
In the competitive e-commerce landscape, distinguishing your product through advanced positioning strategies can significantly impact your success. Two primary approaches are emotional and functional positioning.
Emotional Positioning:
- Definition: Emotional positioning focuses on how a product makes the customer feel. It leverages emotional triggers to create a connection with the audience.
- Example: Apple is a master of emotional positioning. Their marketing emphasizes the lifestyle and creativity that come with owning an Apple product, rather than just its technical specs.
- Benefit: This approach can build strong brand loyalty and higher customer engagement. According to a study by Harvard Business Review, emotionally connected customers are more than twice as valuable as highly satisfied customers.
Functional Positioning:
- Definition: Functional positioning highlights the practical benefits and features of a product. It focuses on solving a specific problem or fulfilling a need.
- Example: Dyson’s vacuum cleaners are positioned around their superior technology and efficiency in cleaning.
- Benefit: This approach attracts customers looking for specific solutions and can justify premium pricing based on product performance.
8.2 Positioning in Saturated Markets
Saturated markets present a unique challenge where differentiation is crucial for survival and growth. Here are strategies to position your product effectively in such competitive environments:
- Niche Targeting: Focus on a specific niche within the market where competition might be lower. For example, instead of competing broadly in the apparel market, you could target eco-friendly yoga wear.
- Innovation and Unique Features: Introduce innovative features that set your product apart. Tesla, for instance, revolutionized the automotive market with its electric cars and advanced autopilot features.
- Superior Customer Experience: Offer unparalleled customer service to differentiate your brand. Zappos is renowned for its exceptional customer service, which has become a core part of its brand identity.
- Brand Storytelling: Create a compelling brand story that resonates with your audience. TOMS Shoes’ narrative of social responsibility through their one-for-one model has created a loyal customer base.
- Value Proposition: Clearly articulate your unique value proposition. Warby Parker differentiates itself in the eyewear market with stylish, affordable glasses and a home try-on program.
Statistics:
- Customer Loyalty: According to a study by Accenture, 83% of customers who feel an emotional connection to a brand will continue to buy from that brand.
- Market Penetration: Innovative products in saturated markets can achieve rapid penetration. For example, Dollar Shave Club captured 10% of the razor market within a few years of launching.
8.3 Product Lifecycle Positioning
Understanding and adapting your positioning strategy throughout the product lifecycle stages can enhance your product’s market performance and longevity.
Introduction Stage:
- Strategy: Focus on building awareness and generating interest. Highlight the unique benefits and use aggressive marketing tactics.
- Example: When launching the iPhone, Apple focused on its groundbreaking features and sleek design through high-impact advertising.
Growth Stage:
- Strategy: Emphasize differentiation from competitors as market awareness grows. Expand distribution channels and optimize pricing strategies.
- Example: Spotify, during its growth phase, highlighted its vast music library and personalized playlists to differentiate from other streaming services.
Maturity Stage:
- Strategy: Strengthen customer loyalty and explore market expansion. Introduce product variations to maintain interest.
- Example: Coca-Cola continuously introduces new flavors and packaging to keep the product fresh and engaging in the maturity stage.
Decline Stage:
- Strategy: Consider repositioning or rejuvenating the product. Explore cost-cutting measures or prepare for product discontinuation.
- Example: Kodak attempted to reposition itself from film to digital photography and printing services as the film market declined.
Product Lifecycle Metrics:
- Introduction: Market penetration rate, initial sales figures.
- Growth: Market share, customer acquisition rates.
- Maturity: Repeat purchase rates, brand loyalty metrics.
- Decline: Market exit strategy efficiency, cost management.
By applying these advanced positioning strategies, new e-commerce entrepreneurs can effectively navigate and succeed in complex market environments. Whether leveraging emotional appeal, innovating in saturated markets, or strategically managing the product lifecycle, these approaches can significantly enhance your product’s market positioning and overall business success.
Practical Examples and Case Studies

9.1 Product Positioning Examples in E-Commerce
Effective product positioning can transform an ordinary product into a market leader by strategically defining its place in the market and in the minds of consumers. Here are a few notable examples from the e-commerce world:
- Warby Parker: This eyewear brand entered the market with a clear value proposition: stylish, affordable glasses with the convenience of online shopping. Their innovative home try-on program allowed customers to try five frames for free before purchase, addressing a significant pain point in online eyewear shopping. This unique selling proposition (USP) set Warby Parker apart in a crowded market and established them as a major player in online retail.
- Dollar Shave Club: Dollar Shave Club disrupted the razor market with a subscription model that delivered affordable, high-quality razors directly to consumers. Their memorable launch video emphasized convenience and cost savings, effectively positioning them against more expensive, traditional brands like Gillette.
- Glossier: Glossier’s positioning revolves around simplicity and authenticity. They leveraged user-generated content and focused on a minimalistic approach to beauty, appealing to millennials and Gen Z. Their direct engagement with customers on social media helped build a strong, loyal community around the brand.
9.2 Case Studies on Successful Product Positioning
Case Study: Amazon Prime
Challenge: In the early 2000s, Amazon wanted to increase customer loyalty and repeat purchases.
Strategy: Amazon introduced Amazon Prime, a subscription service offering free two-day shipping on eligible items. This positioned Amazon as the go-to platform for convenience and quick delivery.
Outcome: Amazon Prime significantly boosted customer retention and average spend per customer. According to a Consumer Intelligence Research Partners (CIRP) report, Prime members spend an average of $1,400 per year compared to $600 for non-Prime members. This strategy not only increased sales but also solidified Amazon’s market dominance.
Key Takeaways:
- Convenience: Providing a unique benefit like free two-day shipping can drive customer loyalty.
- Subscription Model: Leveraging subscription services can create a steady revenue stream and enhance customer retention.
Case Study: Airbnb
Challenge: Airbnb needed to differentiate itself from traditional hotels and other accommodation platforms.
Strategy: Airbnb’s “Live There” campaign focused on offering unique, authentic travel experiences that allowed guests to live like locals. They highlighted the personal and unique nature of staying in an Airbnb property, contrasting sharply with the standardized experience of staying in a hotel.
Outcome: The campaign successfully repositioned Airbnb as more than just a budget-friendly alternative to hotels. It attracted travelers seeking personalized and immersive experiences, contributing to Airbnb’s rapid growth and market expansion.
Key Takeaways:
- Experience-Based Positioning: Highlighting unique customer experiences can effectively differentiate a brand in a crowded market.
- Emotional Connection: Building an emotional connection with customers can foster brand loyalty and advocacy.
9.3 Lessons from Leading Online Retailers
Leading online retailers have mastered the art of product positioning through innovative strategies and a deep understanding of their target markets. Here are some key lessons:
- Consistent Branding and Messaging: Maintaining a consistent brand voice and messaging across all channels is crucial. For instance, Apple’s brand messaging emphasizes innovation and quality consistently across all its marketing materials, reinforcing its positioning as a premium brand.
- Customer-Centric Approach: Successful retailers prioritize the needs and preferences of their customers. Zappos, for example, is known for its exceptional customer service, which is a core part of its brand identity. This customer-centric approach has built immense customer loyalty and trust.
- Leveraging Data and Analytics: Leading e-commerce businesses use data analytics to understand customer behavior and refine their positioning strategies. Amazon uses extensive data analysis to personalize recommendations and enhance the shopping experience, ensuring they stay ahead of customer needs.
- Innovative Marketing Tactics: Creative and memorable marketing campaigns can significantly impact brand positioning. Old Spice’s rebranding campaign, featuring humorous and attention-grabbing ads, repositioned the brand to appeal to a younger audience, revitalizing its market presence.
- Adaptability: The ability to adapt to market changes and consumer trends is essential. Netflix, originally a DVD rental service, successfully transitioned to a streaming platform and content creator, continuously adapting its positioning to meet evolving consumer preferences.
These practical examples and case studies illustrate the power of strategic product positioning in e-commerce. By learning from these successful brands and implementing similar strategies, new e-commerce entrepreneurs can effectively position their products to capture customer interest and drive long-term success.
Tools and Resources

10.1 Tools for Market and Competitive Analysis
Effective market and competitive analysis are fundamental to developing a successful product positioning strategy in e-commerce. Here are some essential tools that can help you gather insights and make informed decisions:
- Google Analytics:
- Usage: Track website traffic, user behavior, and conversion rates.
- Benefits: Provides insights into customer demographics, preferences, and purchasing patterns. Helps identify high-performing products and optimize marketing strategies.
- SEMrush:
- Usage: Conduct competitive analysis, keyword research, and site audits.
- Benefits: Offers detailed reports on competitors’ online strategies, including their top-performing keywords and traffic sources. Helps you identify market gaps and opportunities for differentiation.
- Ahrefs:
- Usage: Analyze competitors’ backlink profiles, track keyword rankings, and perform site audits.
- Benefits: Helps understand competitors’ SEO strategies and identify opportunities for improving your own search engine rankings.
- BuzzSumo:
- Usage: Discover content that performs best for any topic or competitor.
- Benefits: Identifies trending content and influencers in your niche. Helps you create engaging content and build strategic partnerships.
- SurveyMonkey:
- Usage: Conduct customer surveys and gather feedback.
- Benefits: Provides insights into customer satisfaction, preferences, and expectations. Helps tailor your product positioning to better meet customer needs.
Learn about advanced techniques for e-commerce competitive analysis.
10.2 Resources for Product Positioning Strategy Development
Developing a robust product positioning strategy requires a deep understanding of market dynamics and consumer behavior. Here are some valuable resources to guide you:
- Harvard Business Review (HBR):
- Usage: Access articles, case studies, and research on marketing and product positioning.
- Benefits: Offers insights from industry experts and academic research, helping you understand best practices and innovative strategies.
- Statista:
- Usage: Access statistics, reports, and market data.
- Benefits: Provides comprehensive data on market trends, consumer behavior, and industry benchmarks. Helps you make data-driven decisions.
- Nielsen:
- Usage: Access market research reports and consumer insights.
- Benefits: Offers detailed analyses of consumer trends and market dynamics. Helps you identify target markets and refine your positioning strategy.
- HubSpot Blog:
- Usage: Read articles on marketing, sales, and product positioning.
- Benefits: Provides practical tips, strategies, and real-world examples. Helps you stay updated on the latest marketing trends and techniques.
- MarketingProfs:
- Usage: Access articles, webinars, and training on marketing strategies.
- Benefits: Offers expert advice and practical insights into developing effective marketing and positioning strategies.
10.3 Templates for Positioning Statements and Maps
Creating clear and compelling positioning statements and maps is crucial for defining your product’s place in the market. Here are some templates to help you get started:
Positioning Statement Template:
Template:
For [target audience], [product name] is a [market category] that provides [unique benefit]. Unlike [primary competitor], [product name] offers [unique selling proposition (USP)] because [reasons to believe].
Example:
For eco-conscious consumers, EcoClean is a household cleaning product that provides effective, chemical-free cleaning. Unlike conventional cleaning products, EcoClean offers a 100% natural and biodegradable solution because of its plant-based formula.
Perceptual Map Template:
Template: Use a two-axis graph to plot competitors and your product based on key attributes such as price and quality, innovation and usability, or luxury and affordability.
Example: A perceptual map for the smartphone market could plot price (low to high) on the x-axis and innovation (low to high) on the y-axis, helping visualize where different brands like Apple, Samsung, and OnePlus stand.
SWOT Analysis Template:
Template:
Strengths: [List your product’s strengths]
Weaknesses: [List your product’s weaknesses]
Opportunities: [List market opportunities]
Threats: [List potential threats]
Example:
Strengths: High-quality materials, strong brand reputation
Weaknesses: Higher price point, limited distribution channels
Opportunities: Growing demand for eco-friendly products, expansion into new markets
Threats: Increasing competition, changing consumer preferences
Utilizing these tools and resources can significantly enhance your ability to develop, implement, and refine a successful product positioning strategy. By leveraging market analysis tools, accessing valuable resources, and using practical templates, you can ensure your product stands out in the competitive e-commerce landscape.
Conclusion
11.1 Recap of Key Points
Mastering product positioning in e-commerce is vital for new retailers aiming to stand out in a crowded online market. Here’s a recap of the key points discussed throughout this guide:
- Understanding Product Positioning: It’s about defining where your product fits in the market and how it’s perceived by your target customers. Effective positioning can drive brand loyalty and customer satisfaction.
- Developing a Product Positioning Strategy: This involves identifying your target market, analyzing competitors, defining your unique selling proposition (USP), and communicating it clearly through a brand positioning statement.
- Identifying Target Markets: Utilize market segmentation to understand and target specific customer groups. Create customer-centric positioning that resonates with their needs and preferences.
- Differentiating Your Products: Highlight the unique benefits of your product. Strategies include focusing on quality, customization, customer service, and sustainability.
- Crafting a Positioning Statement: A concise statement that encapsulates your product’s value, target market, and key benefits. This guides all your marketing and branding efforts.
- Implementing Product Positioning: Strategically place your product in the market using channels, partnerships, SEO, and advertising. Techniques include storytelling, content marketing, and personalization.
- Evaluating and Refining Your Positioning: Regularly assess and adjust your positioning strategy based on customer feedback, sales data, market trends, and competitor activities.
- Advanced Positioning Strategies: Employ emotional and functional positioning, navigate saturated markets, and adapt your strategy through the product lifecycle stages.
- Practical Examples and Case Studies: Learn from successful brands like Warby Parker, Dollar Shave Club, and Airbnb, and understand the importance of consistent branding and customer-centric approaches.
- Tools and Resources: Use tools like Google Analytics, SEMrush, and HubSpot, and leverage resources like Harvard Business Review and Statista to develop and refine your positioning strategy.
11.2 Final Thoughts on Product Positioning in E-Commerce
Product positioning is more than just a marketing tactic; it’s a strategic approach that influences every aspect of your business. For new e-commerce retailers, mastering product positioning means deeply understanding your customers, continuously innovating, and maintaining a consistent brand image.
Successful product positioning can transform your online business by creating a strong connection with your audience and differentiating your products from competitors. It’s about finding that unique space in the market where your product not only meets a need but does so in a way that resonates deeply with your target customers.
11.3 Future Trends in Product Positioning
As the e-commerce landscape continues to evolve, staying ahead of trends in product positioning is crucial. Here are some future trends to watch:
- Personalization and AI: Leveraging artificial intelligence to provide personalized shopping experiences will become increasingly important. Personalized product recommendations and dynamic content tailored to individual preferences will enhance customer engagement and loyalty.
- Sustainability and Ethical Positioning: As consumers become more environmentally conscious, positioning products around sustainability and ethical practices will gain prominence. Brands that can authentically communicate their commitment to these values will attract and retain loyal customers.
- Augmented Reality (AR): AR will play a significant role in product positioning, especially in industries like fashion and home decor. Providing virtual try-ons and interactive product experiences can differentiate your brand and enhance the online shopping experience.
- Omni-Channel Integration: Seamlessly integrating online and offline experiences will be key. Consumers expect a consistent brand experience whether they are shopping online, via mobile, or in-store. Brands that can provide a cohesive omni-channel experience will stand out.
- Data-Driven Positioning: Utilizing big data and advanced analytics to understand consumer behavior and preferences will enable more precise and effective positioning strategies. Predictive analytics can help anticipate market trends and consumer needs.
Statistics and Insights:
- According to a report by Grand View Research, the global artificial intelligence in retail market size is expected to reach USD 19.37 billion by 2027, highlighting the growing importance of AI in personalized shopping experiences.
- A Nielsen report found that 73% of global consumers would definitely or probably change their consumption habits to reduce their environmental impact, underscoring the importance of sustainability in product positioning.
Mastering product positioning in e-commerce requires a strategic, customer-focused approach. By understanding and leveraging advanced positioning strategies, new retailers can effectively navigate the competitive landscape and build a strong, lasting brand. Stay ahead of future trends, continually refine your strategy, and always prioritize your customers’ needs and preferences to ensure long-term success.